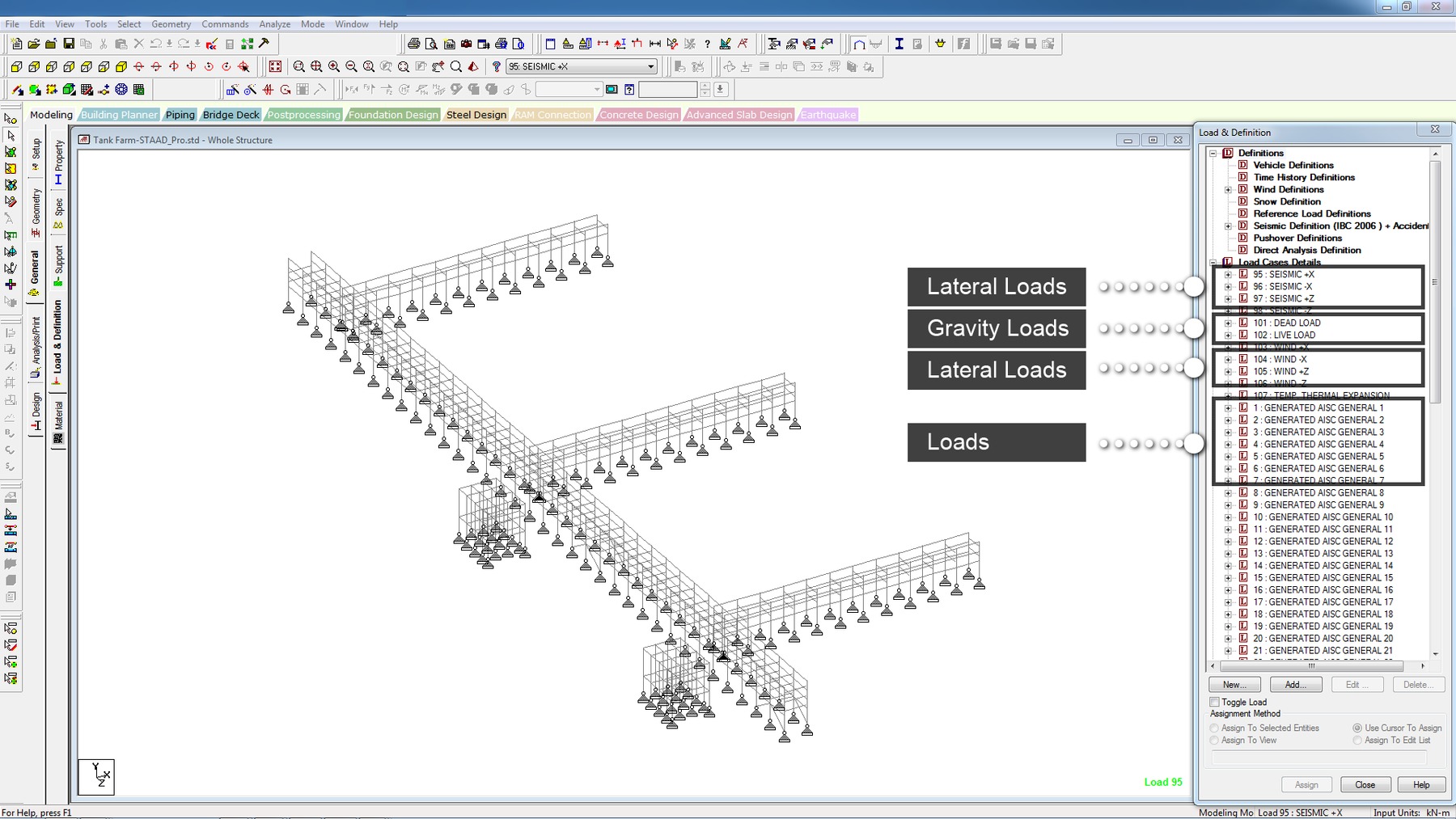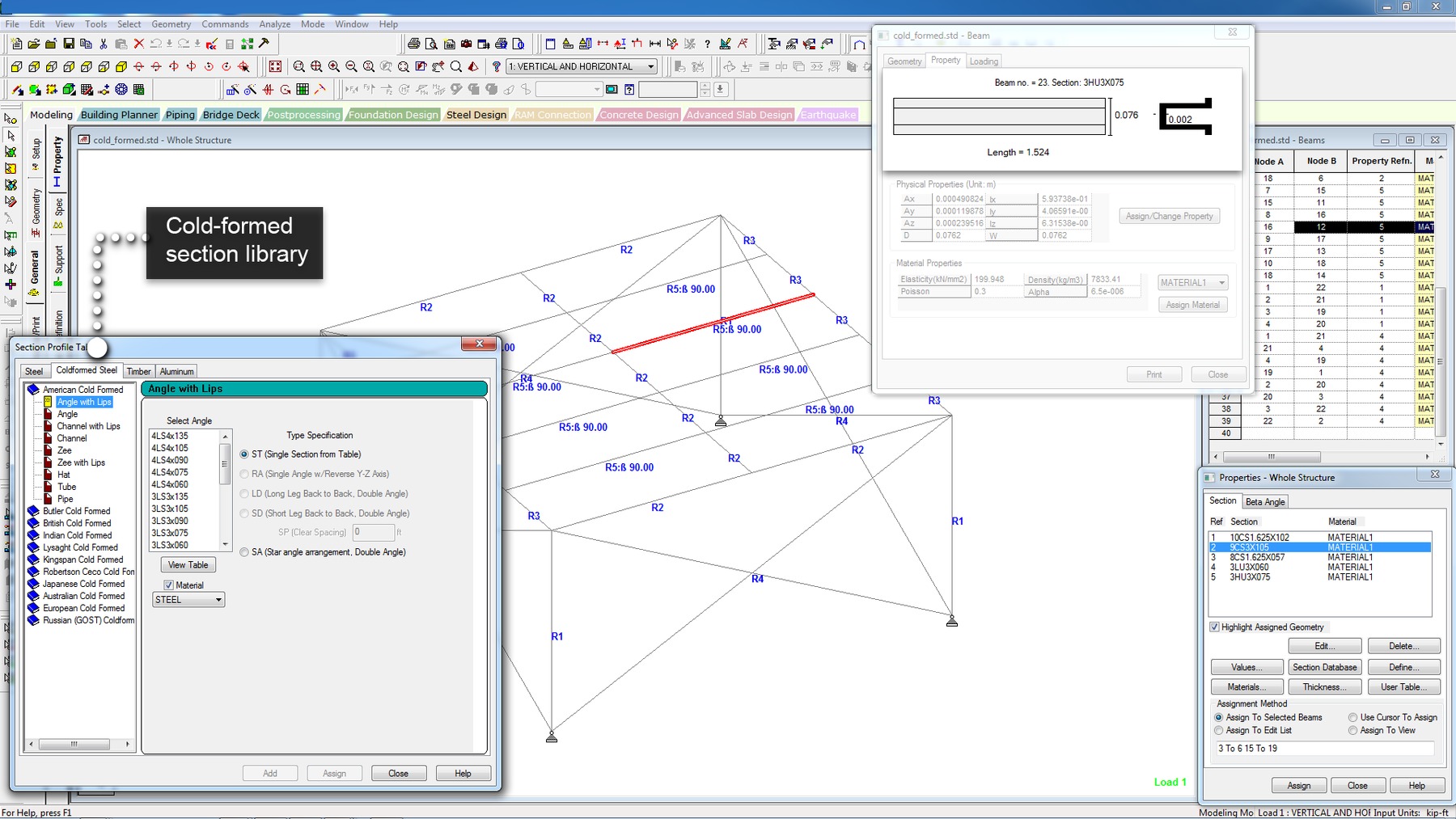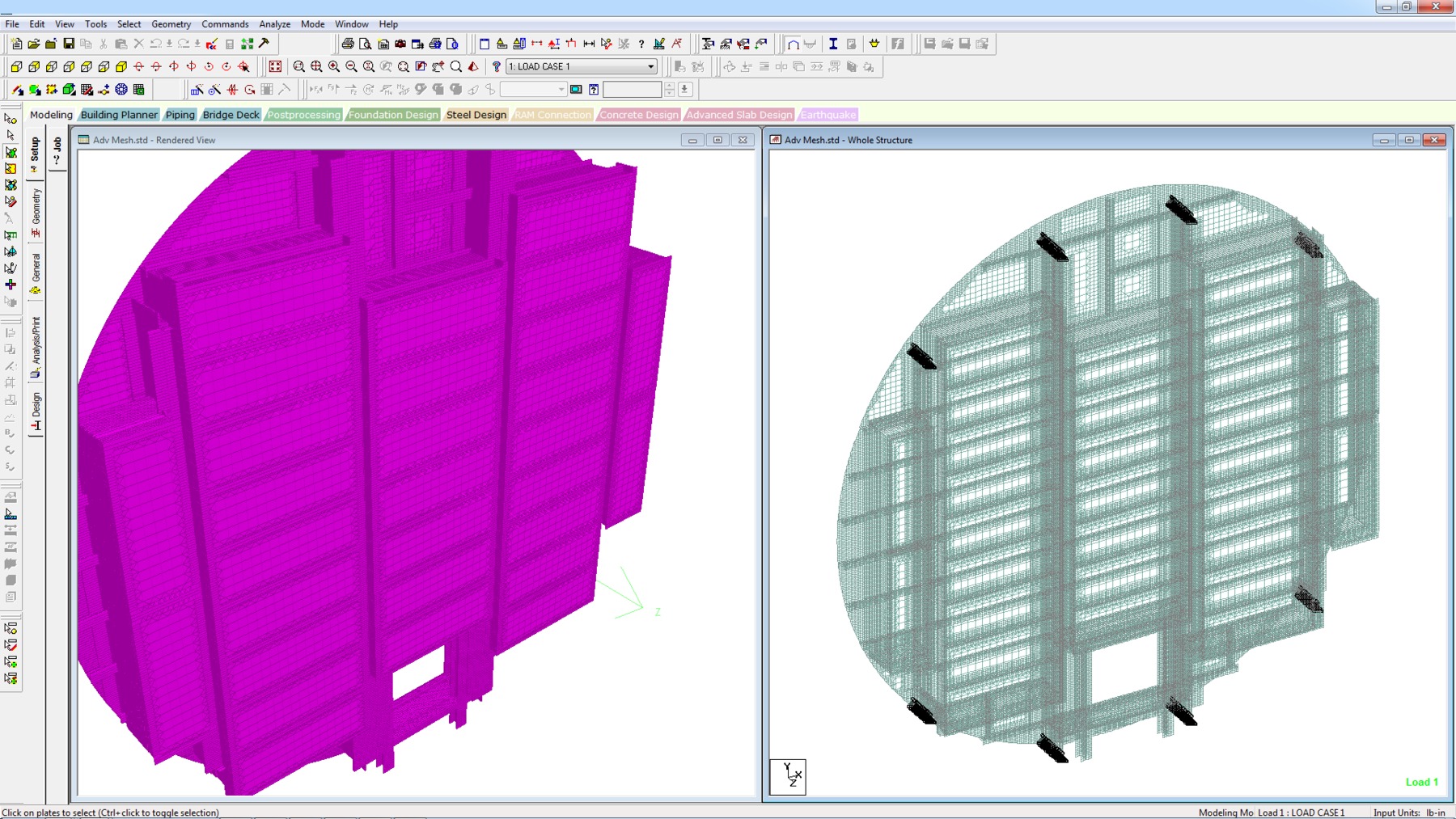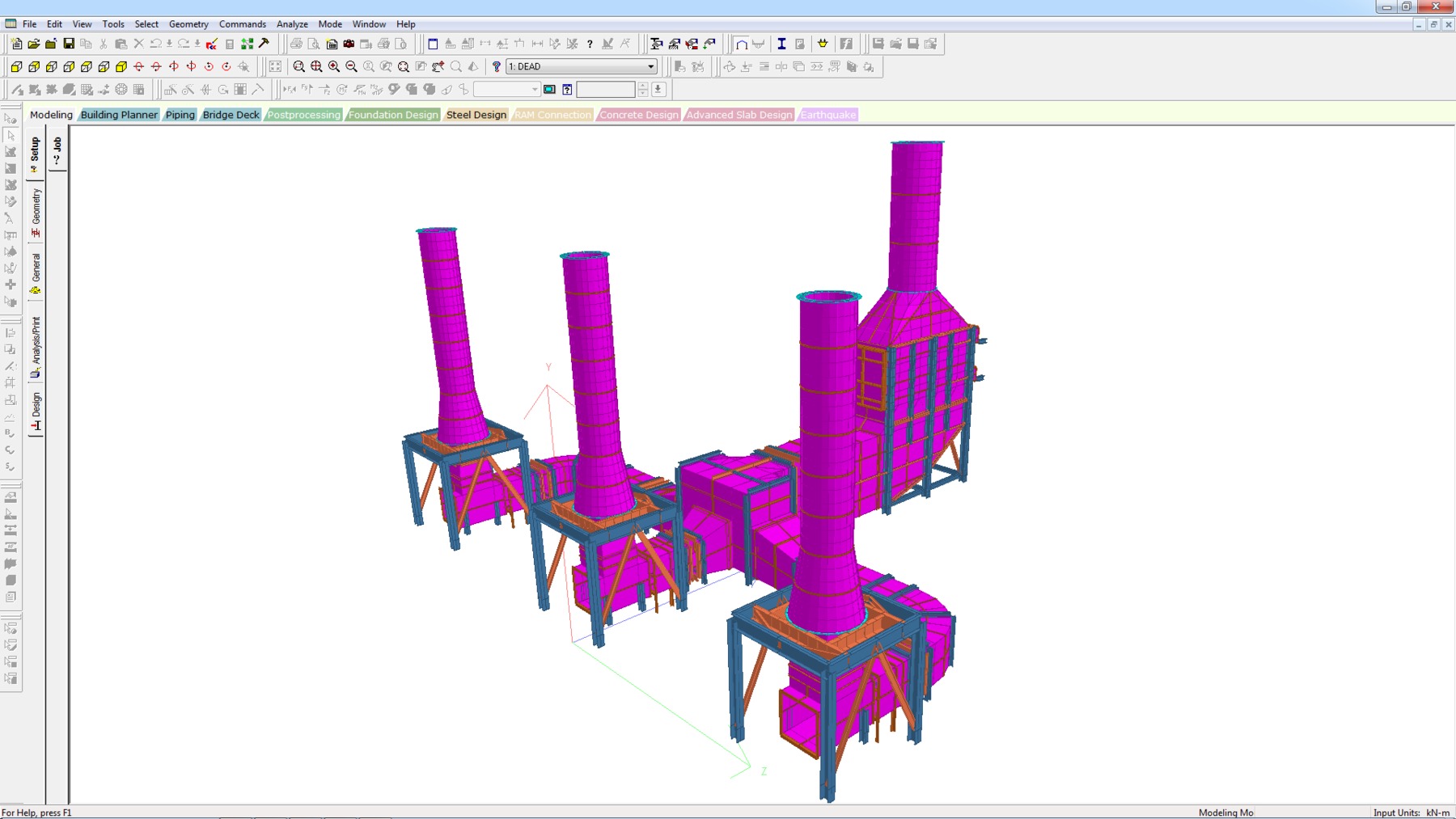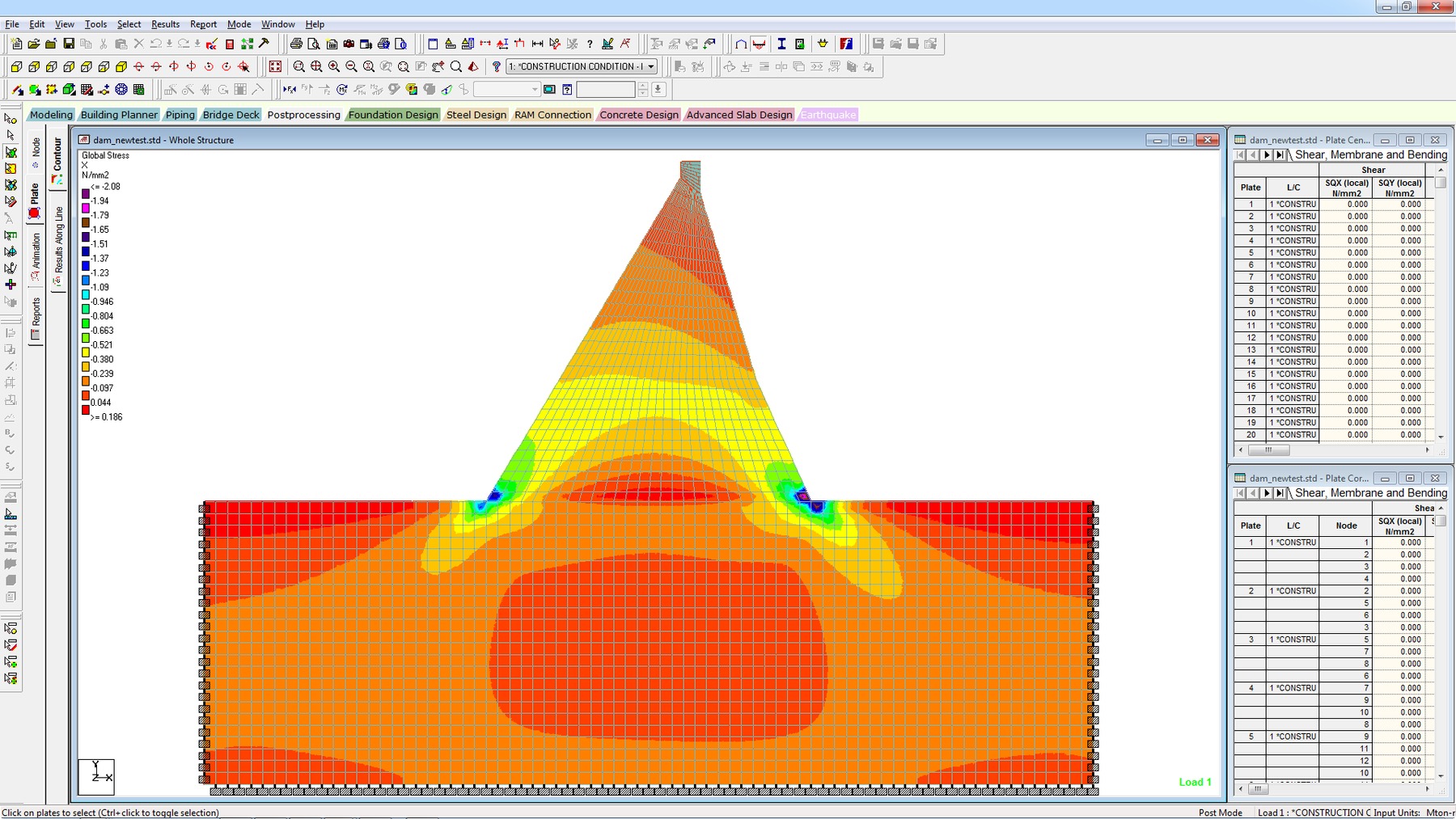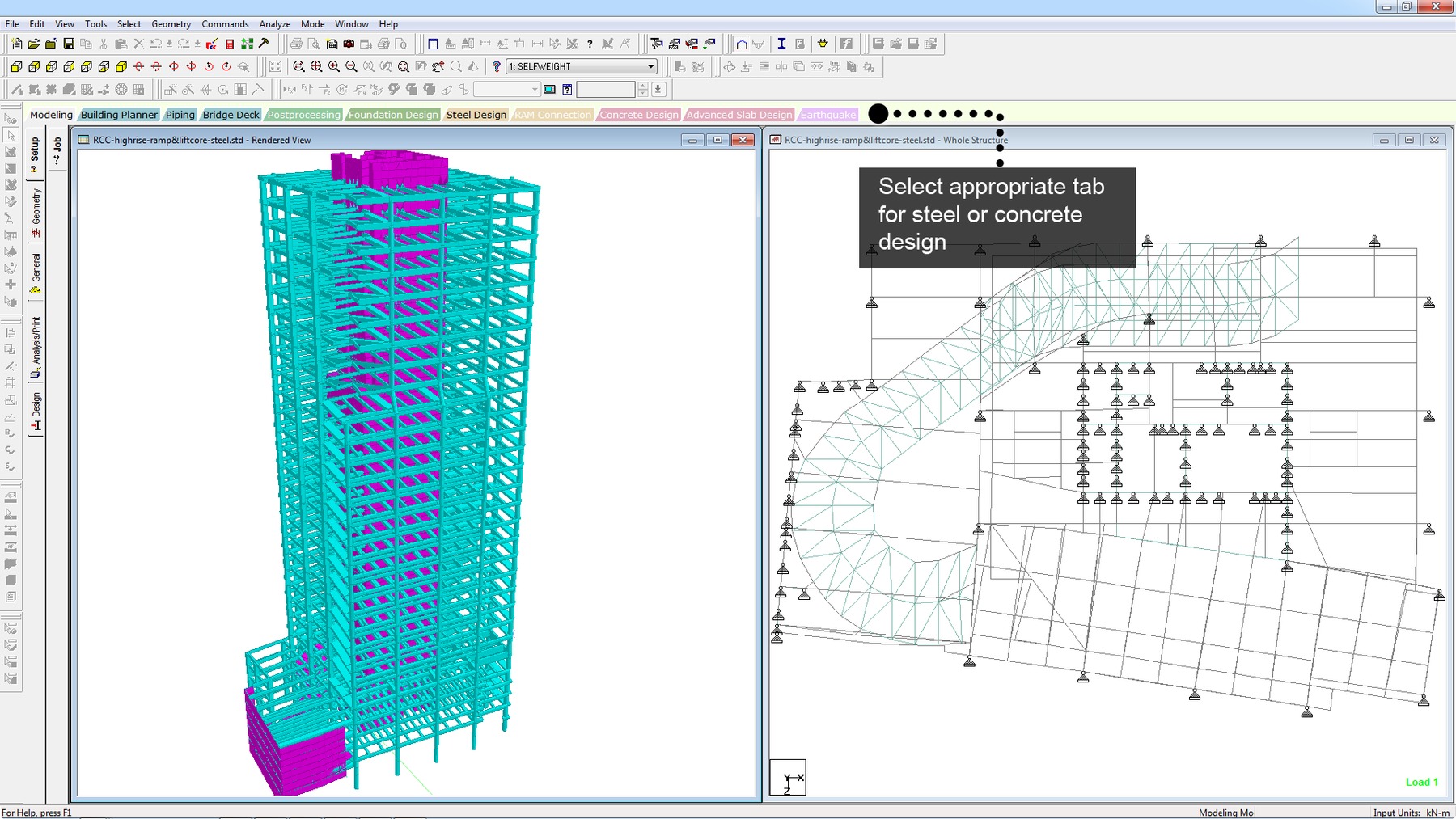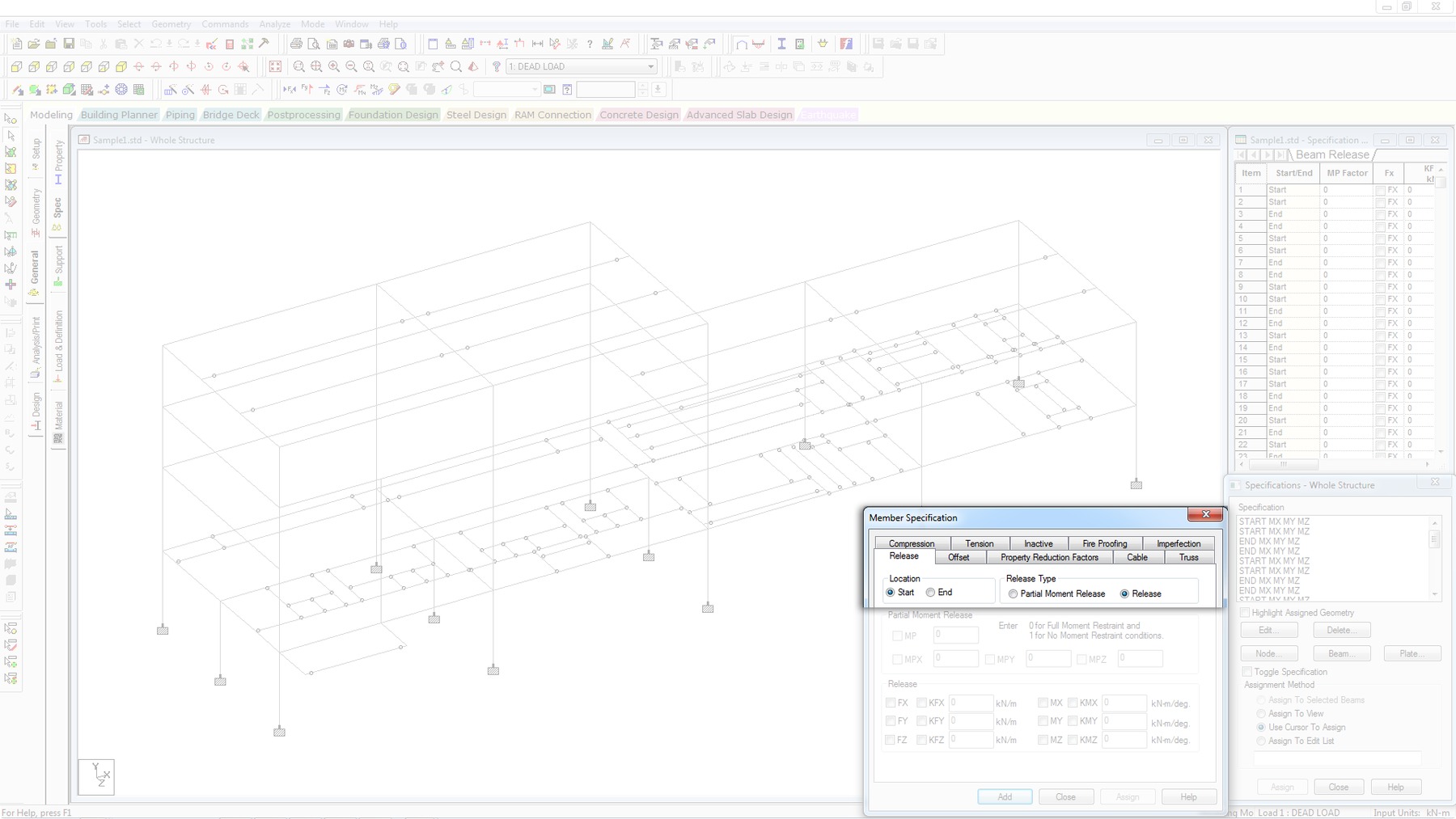
STAAD.Pro - Analysis Capabilities
Static, P-Delta, Non-Linear Analyses
- Linear, P-Delta analysis
- Non-linear analysis with automatic load and stiffness correction
- Multiple analysis in same run
- True curvilinear beams (not piecewise linear)
- Plate elements contain extra “drilling” degree of freedom
- Tapered tubular cross-sections such as hexagonal, octagonal, etc. (excellent for poles)
- Unidirectional support (compression-only/tension-only supports) for generation of soil springs
- Master/slave capabilities
- I-beam warping end restraint added as an option for torsional stiffness
- Buckling analysis
- Plate elements consider inclined supports
- Member and spring specification
- Fixed, pinned and spring supports with releases. Also Inclined Supports
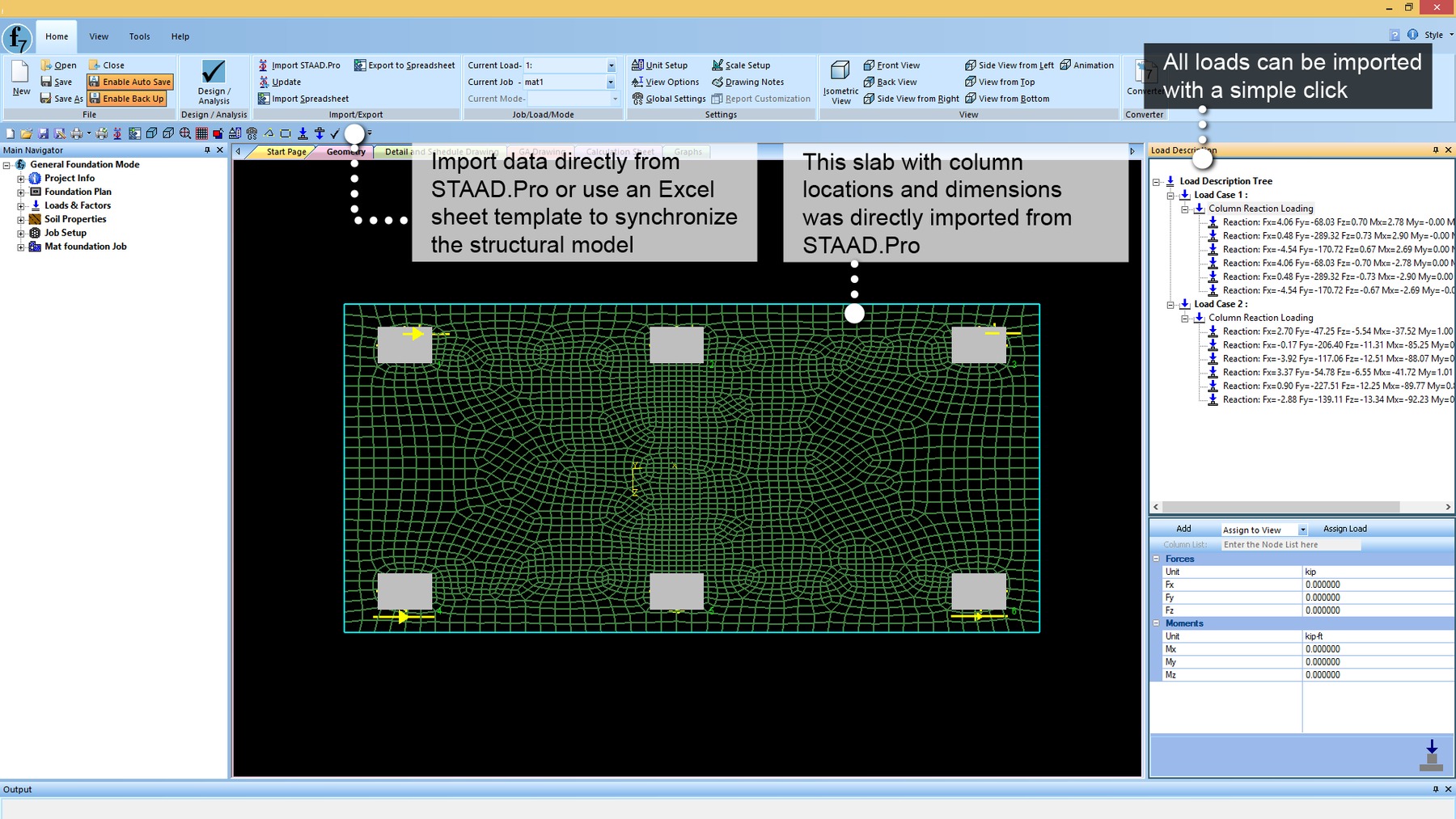
- Automatic spring support generator for mat foundations
- Active/Inactive members for load-dependent structures
- Compression-only and tension-only members, multi-linear (non-linear) spring supports
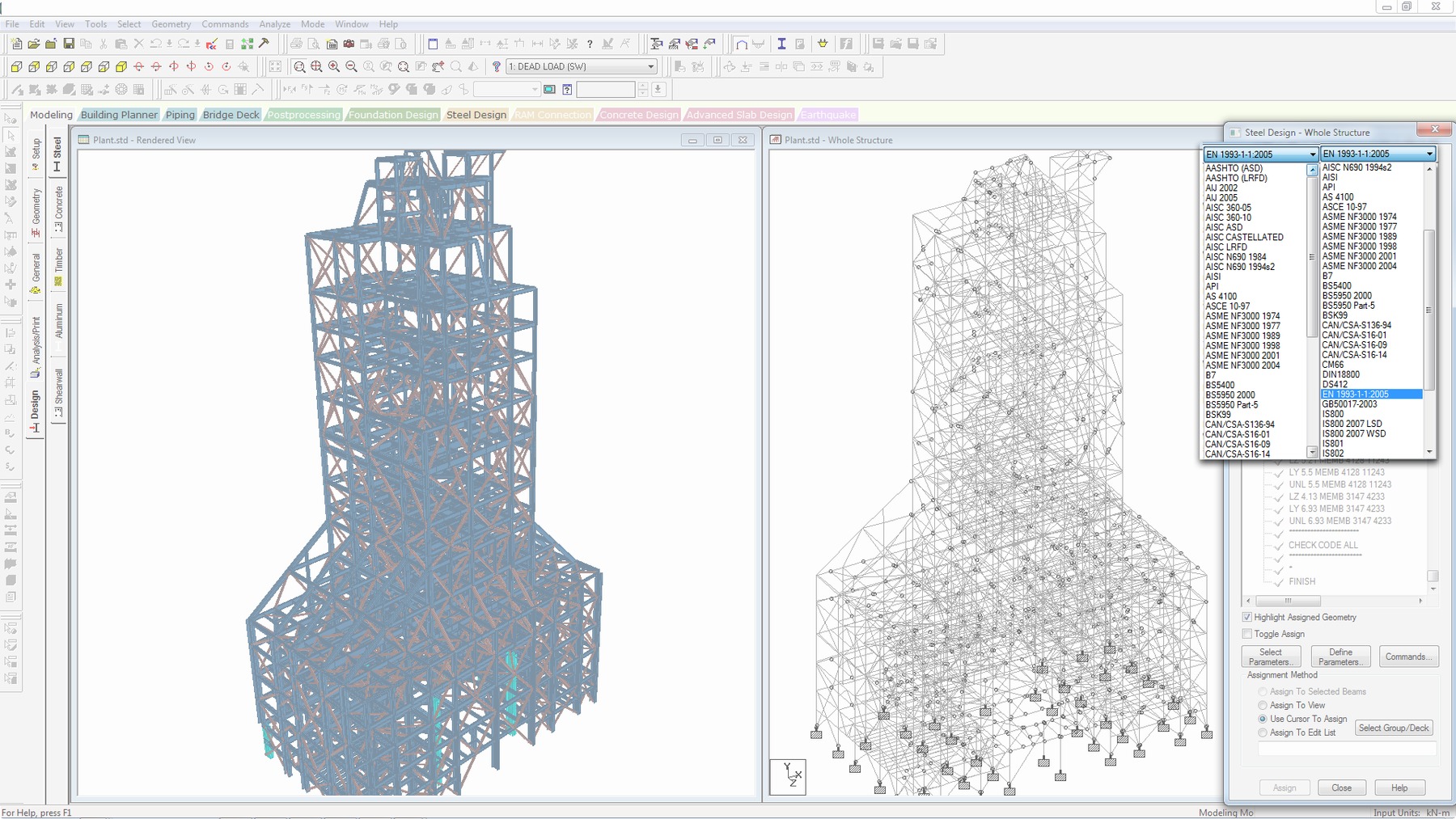
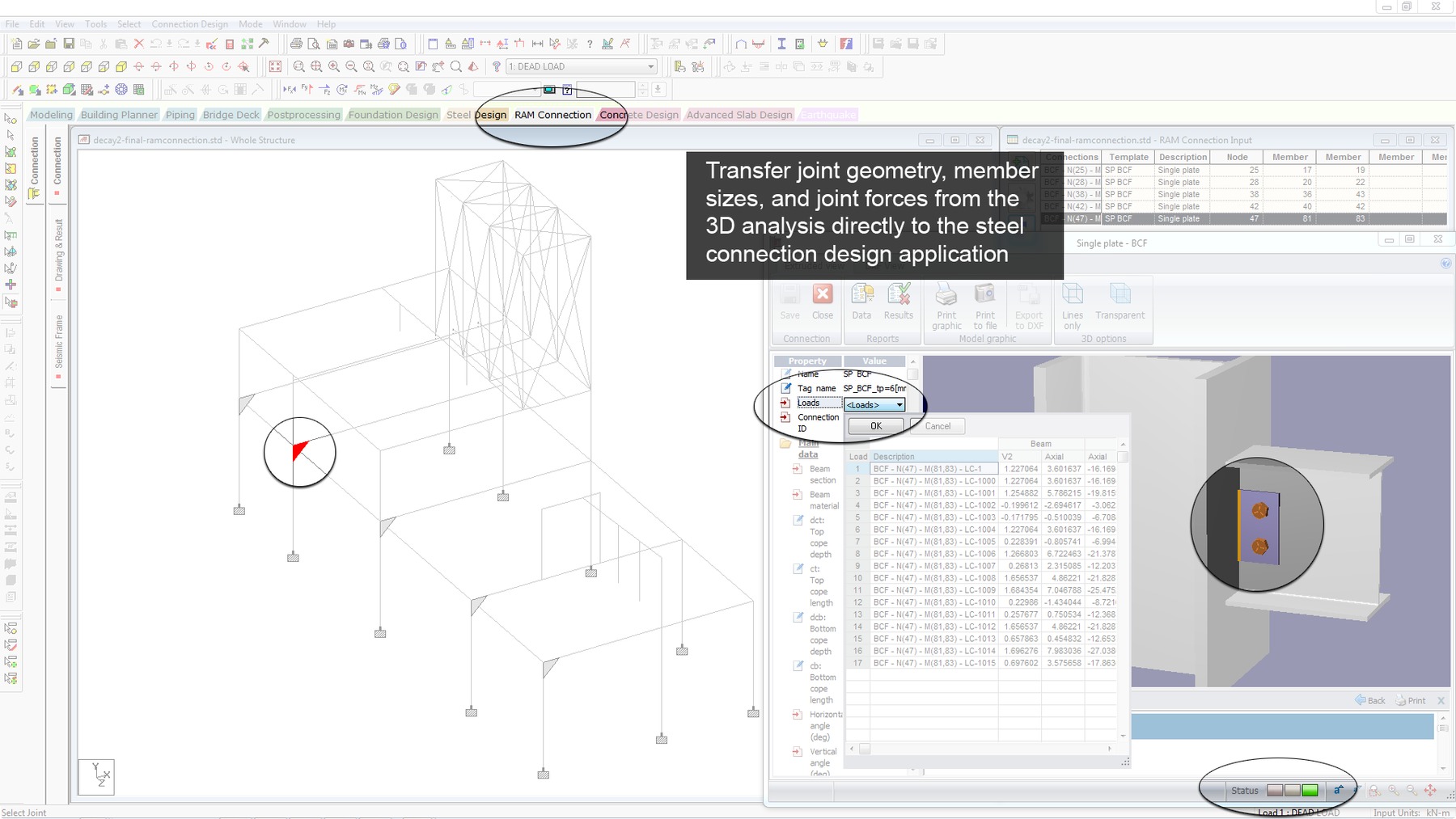
- CIMSTEEL interface
- 3D beam stress manager for calculation of combined stresses on a member
- Member tension command can be used with IBC/UBC load generator
- Determine stresses and forces along any cut line through a group of plates by cutting with a plane
- Elbows (curved beams with pipe sections) can be modeled with an internal pressure
- Multi-linear spring curves can be assigned to elastic or plate mats
- Beam, truss, tapered beam, shell/plate bending/plane stress and 8-noded solid elements
- Full and partial moment releases (excellent for steeel frames where releases defined by springs are hard to determine)
- Nonlinear cable members for cables
- P-Delta analysis enabled for plates
- New automated bridge loader to calculate 3D influence surfaces, traffic lanes, critical vehicle loading positions, etc. (optional)
- Influence area reported for spring supports for elastic mats
- Warnings for “load losses” due to poorly defined beam releases
- Enhanced solid stress contour definition for brick elements
Dynamic Analysis
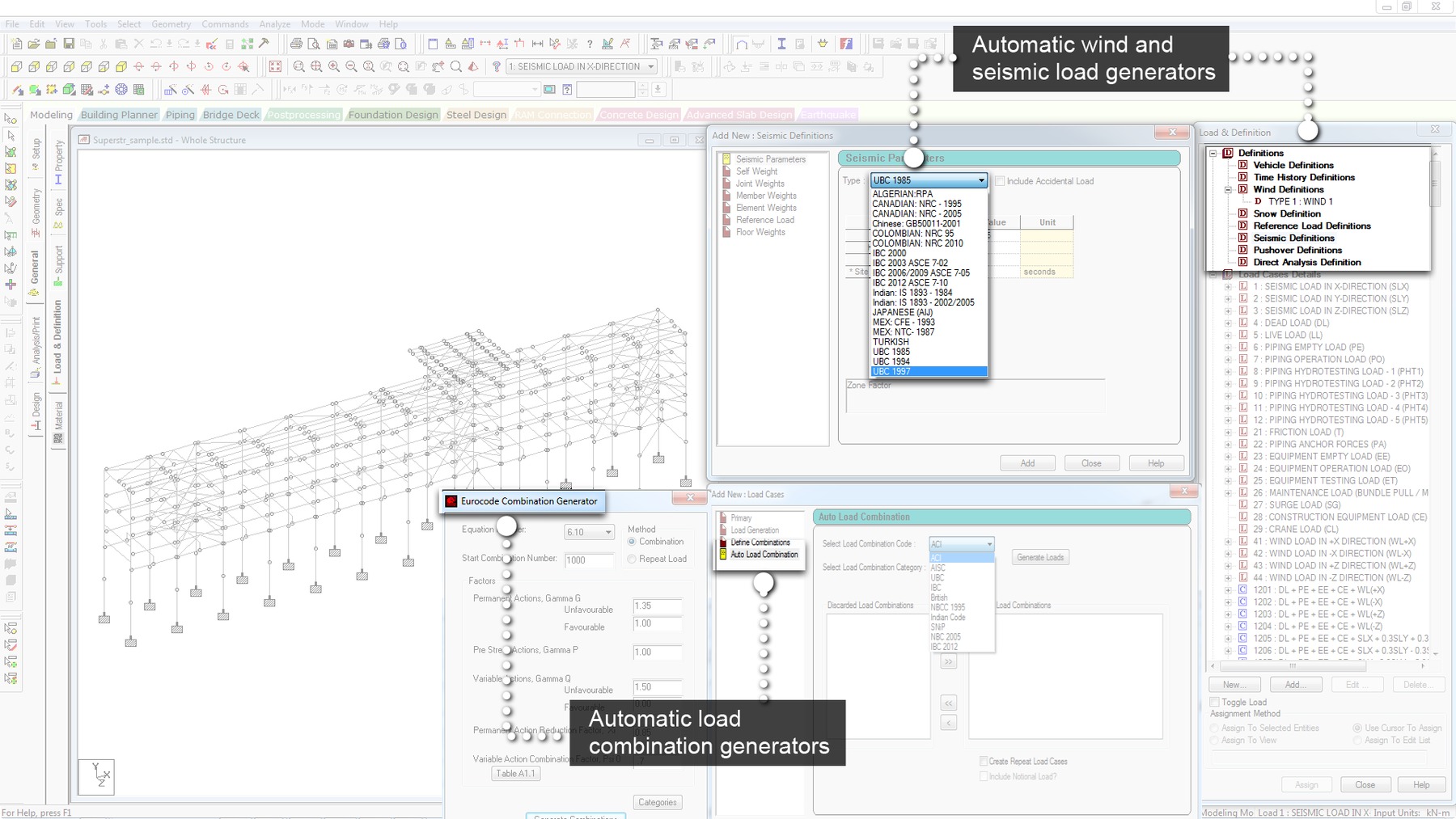
- UBC 94, 97 and IBC 2000 and IBC 2003 supported
- Calculation of maximum base shear for time history loading
- Scale factors for ground acceleration for time history loading
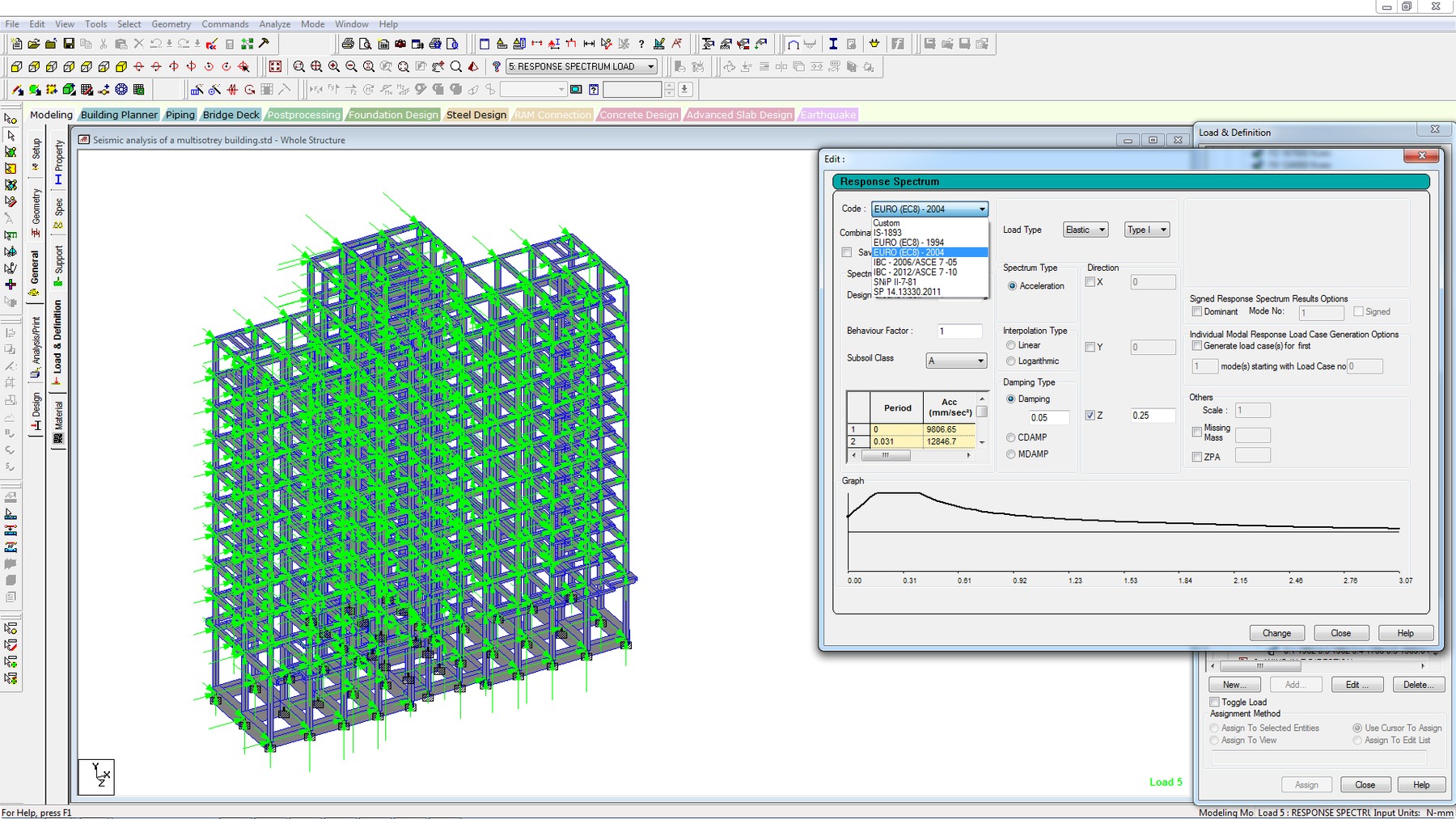
- Response Spectrum
- Time History Analysis with blast loading and multiple arrival times for multiple vibrational sources
- Harmonic Load Generator
- Combination of Dynamic Forces with Static Loading for subsequent Design
- Missing mass for response spectrum load cases
- Logarithmic interpolation for spectra
- Modal damping for time history and spectrum
- Composite damping to specify damping ratio for each member/element
- Base shear calculation includes direction factors
- Extraction of Frequency and Mode Shapes
- Modal Damping Ratio for Individual Modes
- Generate floor spectra from time history